-
Free from additives and fillers
-
Gluten Free
-
HPLC Lab tested
-
Non-GMO
-
Science backed
-
Vegan
Scientifically Tailored Ingredients
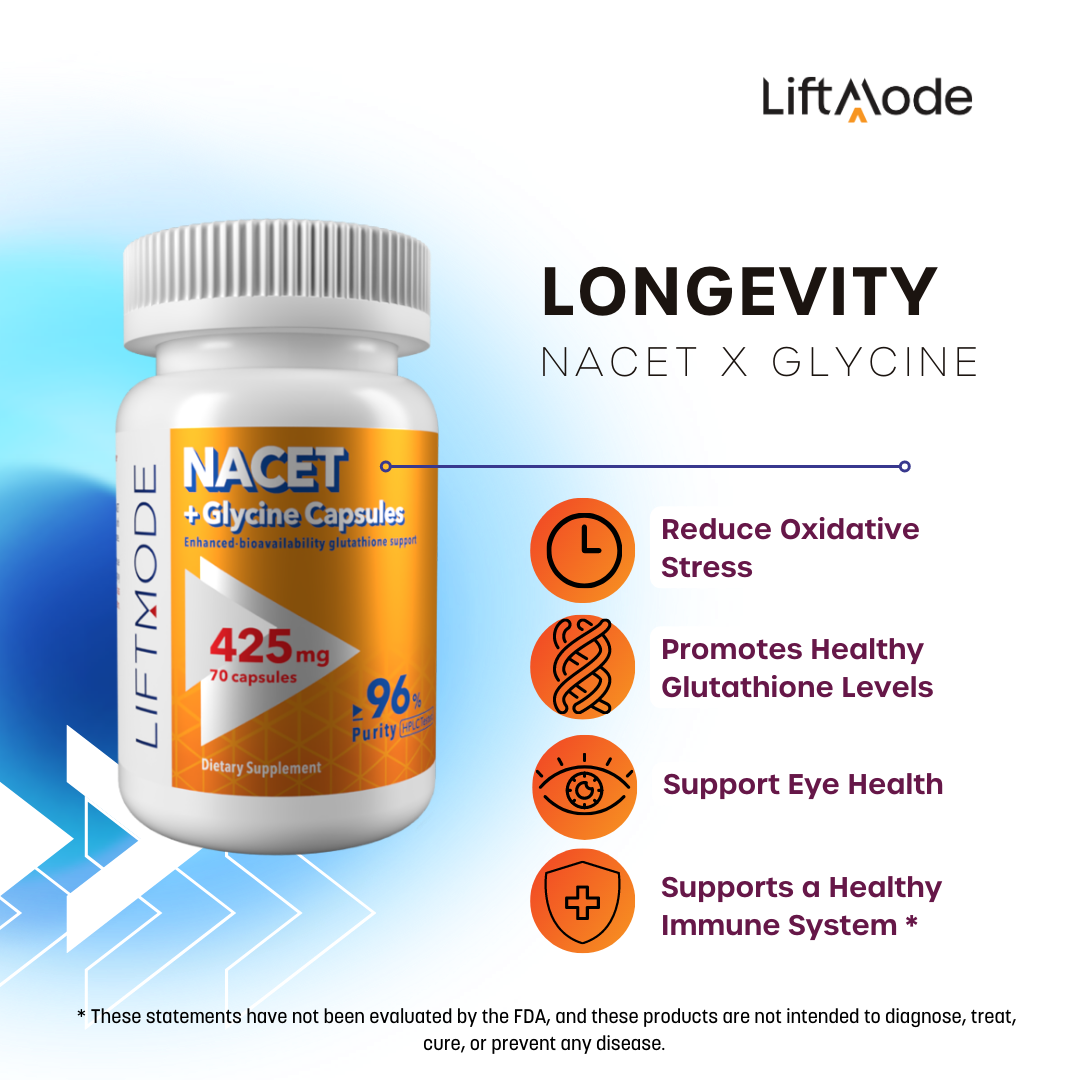
NACET (N-Acetyl L-Cysteine Ethyl Ester)

NACET (N-Acetyl L-Cysteine Ethyl Ester)
NACET is an N-Acetyl L-Cysteine amino acid (pictured to the left) with an added ethyl ester group. Studies have indicated that the additional ester group enhances cellular uptake and bioavailability. NACET is best-known for its ability to improve intracellular glutathione levels. In effect, NACET has fascinating antioxidant properties to help support healthy ageing. Studies have indicated that NACET’s antioxidant effects are also potent in the eyes, where it protects retinal cells against oxidative damage. - Enhanced bioavailability form of N-Acetyl L-Cysteine (NAC) - Improves intracellular glutathione levels, powerful antioxidant - Protects retinal cells against damage and supports healthy ageing
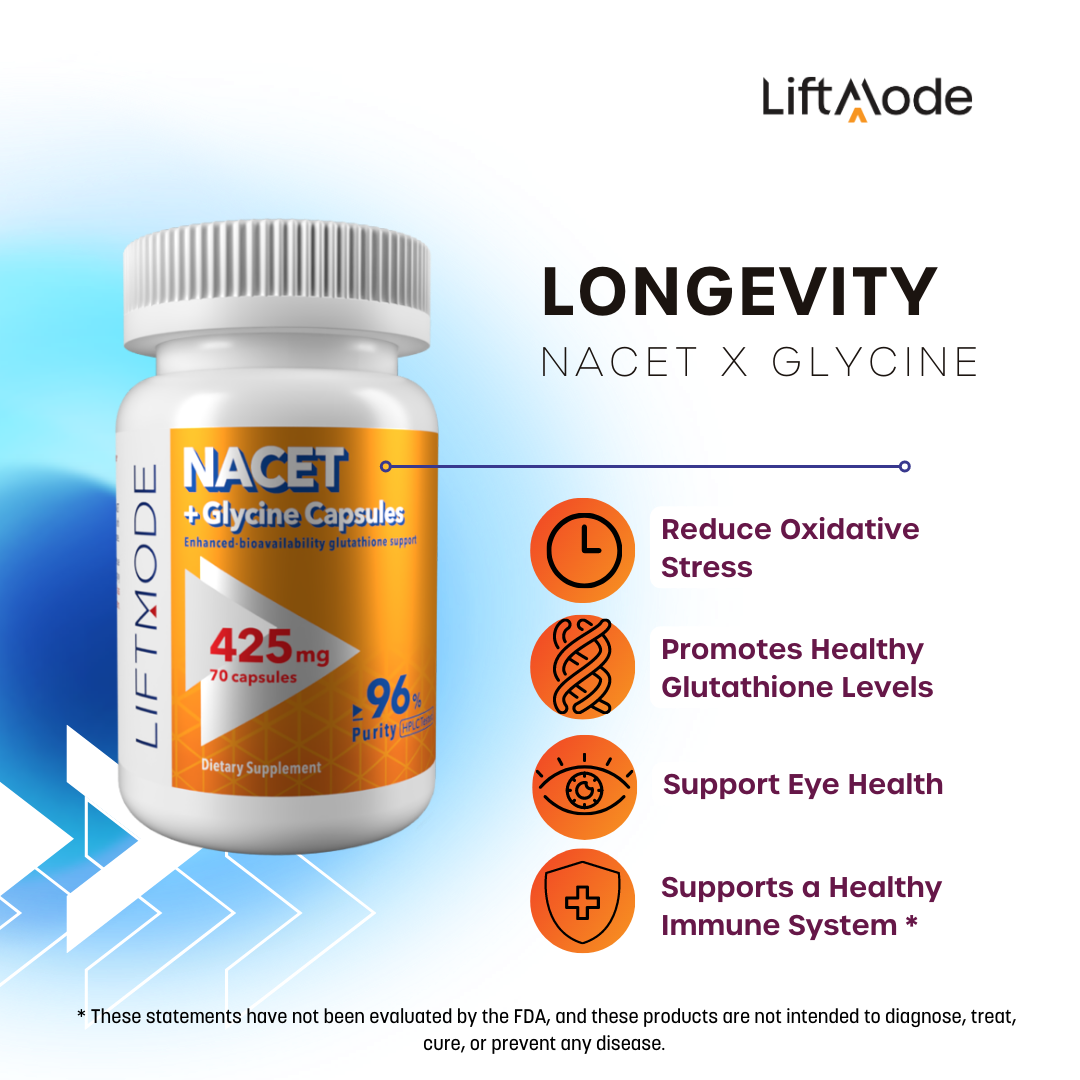
Glycine

Glycine
Glycine is a naturally occurring precursor amino acid to glutathione. It can be found in naturally occurring sources of protein such as meat, dairy, and legumes. It is a powerful scavenging antioxidant that may help reduce oxidative stress inside cells and may help reduce age-related glutathione deficiency. Glycine supplementation has been found to increase tissue glutathione levels in some studies, while also supporting connective tissue and joint health. Other research has indicated that glycine may help improve mood and sleep quality, by increasing extracellular serotonin. Glycine may help boost glutathione levels, support healthy joints and reduce oxidative stress. Glycine may help promote relaxation for healthy stress management. Influx of calcium through the cell membrane is mediated by glycine-gated channel.
Collapsible content
References
References