-
Free from additives and fillers
-
Gluten Free
-
HPLC Lab tested
-
Science backed
Scientifically Tailored Ingredients
Vitamin A

Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a group of compound that include retinal, retinol, and provitamin A carotenoids. Retinyl palmiate is the most abundant form of stored vitamin A in animals, and is a pre-formed version of vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential for healthy eyes: it helps maintain a healthy cornea, is an essential component of rhodopsin (which allows night-time vision), and helps to support and preserve eyesight in the ageing process. - Essential for a clear, healthy cornea - Component of rhodopsin, which allows for night-time vision - Helps to protect and preserve the eyes in ageing
Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)

Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)
Ascorbic Acid (or Vitamin C) is an essential vitamin, which is required through diet for healthy physiological function. Vitamin C plays an important role in collagen production and skin health. On top of this, Vitamin C is involved in catecholamine production, neuroprotection, stress relief and has antioxidant properties. * Essential Vitamin * Stress Relief * Supports Healthy Immune System
Vitamin D

Vitamin D
A fat-soluble steroidal vitamin that is used in the body for improving the absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate. It modulates both the innate and acquired immune systems. Vitamin D receptors are expressed on helper-T cells, B cells and antigen bodies. - Promotes Natural Enzyme Function - Enhances white blood cell activity - Reduces susceptibility to infection
Vitamin E

Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an essential vitamin in the AREDS set of vitamins and minerals for healthy eyes. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant and helps protect your eyes against the negative effects of oxidative stress. The effects of this process accumulate over time, so oxidative stress is linked to ageing. By protecting your eyes against radical oxygen species (ROS), vitamin E helps to ensure longevity. - Potent antioxidant and healthy ageing effects - Works synergistically with other AREDS nutrients - Protects the eyes against oxidative damage
Zinc

Zinc
Zinc citrate represents a highly-bioavailable form of elemental zinc. Zinc is essential for the immune system and is a component of around 300 enzymes and 2000 transcriptional factors. Each serving delivers approximately 7.1 mg elemental zinc. When used in combination with Quercetin, this helps to form a zinc-ionophore and improves the levels of zinc in your cells. Furthermore, zinc plays an essential role in the macula, supporting healthy eyesight. - Promotes Natural Enzyme Function - Anti-Pathogenic benefits - Forms zinc-Quercetin-ionophores
Selenomethionine

Selenomethionine
An organic form of selenium, with a high bioavailability that also produces methionine when metabolized. Selenium and methionine are hugely popular antioxidant compounds that have demonstrated benefits for the immune system. - Powerful immune support - Potent antioxidant protection - Anti-pathogenic effects
Copper

Copper
Copper is a trace metal that is essential for healthy physiological functions. It is used in variety of enzymes and enzyme cofactors, and is concentrated primarily in the liver, brain, bones, and eyes. It helps with the development of flexible connective tissue in the eye, and binds with zinc to form a copper-zinc complex. - Essential trace metal element for healthy growth and development - Forms zinc-copper complexes that help protect the eye - Important for formation of intraocular flexible connective tissue
Lutein

Lutein
Lutein is a naturally occurring carotenoid that's found in many foods, including egg yolks, dark green leafy vegetables, corn, orange pepper, kiwi fruit, grapes, zucchini, and squash. Lutein is a major component of the retina and macula, the parts of the eye that provide sharp vision. Some studies suggest that lutein may also help with cognitive function, cardiovascular health. Lutein may help protect skin cells from sun damage and slow signs of aging.
Astaxanthin

Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a fat-soluble pigment with powerful antioxidant properties that may play a role in protecting your cells from free radicals and oxidative stress. Astaxanthin is a carotenoid, a group of chemicals that also includes lycopene and beta-carotene. It's known for its antioxidant properties, which may help protect cells from damage. Astaxanthin is produced in algae through a process that involves mimicking photosynthetic conditions, modifying external conditions, and then allowing the algae to accumulate astaxanthin. Astaxanthin, often hailed as the king of antioxidants, is 6,000 times stronger than vitamin C. Astaxanthin may help maintain normal cholesterol levels. Astaxanthin may help prevent dry eyes and soreness, reduce eye strain and fatigue, and increase blood flow to eye tissues.
Zeaxanthin

Zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is thought to function as a light filter, protecting the eye tissues from sunlight damage. Foods rich in zeaxanthin include eggs, oranges, grapes, corn, goji berries, mango, orange pepper, and some other vegetables and fruits. People use zeaxanthin for age-related vision loss. Zeaxanthin has also been shown to have a number of beneficial effects for human health due to its ability to quench free radicals, exert antioxidant effects, as well as help decrease inflammation.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)

Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha Lipoic Acid (RS-Lipoic Acid) is a naturally occurring antioxidant organosulfur compound, necessary for aerobic respiration in animals. It has a wide range of biological effects which include reducing oxidative stress in neurons, increasing mitochondrial output in liver cells. * Supports a Healthy Brain * Powerful Antioxidant * Improves Energy Levels
NACET (N-Acetyl L-Cysteine Ethyl Ester)

NACET (N-Acetyl L-Cysteine Ethyl Ester)
NACET is an N-Acetyl L-Cysteine amino acid (pictured to the left) with an added ethyl ester group. Studies have indicated that the additional ester group enhances cellular uptake and bioavailability. NACET is best-known for its ability to improve intracellular glutathione levels. In effect, NACET has fascinating antioxidant properties to help support healthy ageing. Studies have indicated that NACET’s antioxidant effects are also potent in the eyes, where it protects retinal cells against oxidative damage. - Enhanced bioavailability form of N-Acetyl L-Cysteine (NAC) - Improves intracellular glutathione levels, powerful antioxidant - Protects retinal cells against damage and supports healthy ageing
Royal Jelly
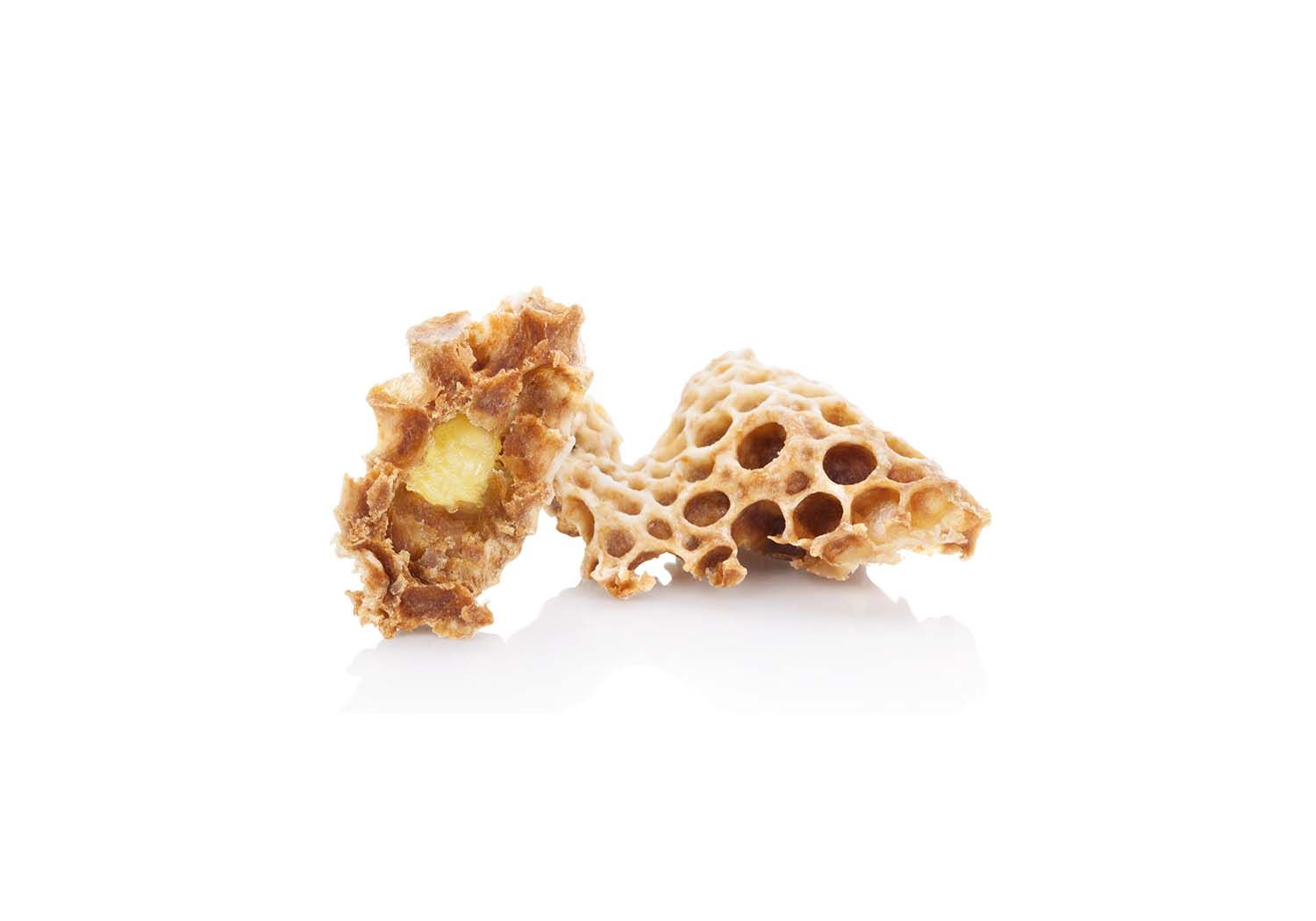

Royal Jelly
Royal Jelly is a secretion from the glands of worker honey bees. Unlike typical “jelly”, Royal Jelly is vegetarian friendly, and can be thought of as similar to honey in its natural source. It has been studied for a variety of health benefits in humans, including to support eye lubrication and prevent dry eyes. - Naturally occurring jelly made by bees - Helps support eye lubrication - Potential antioxidant support
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
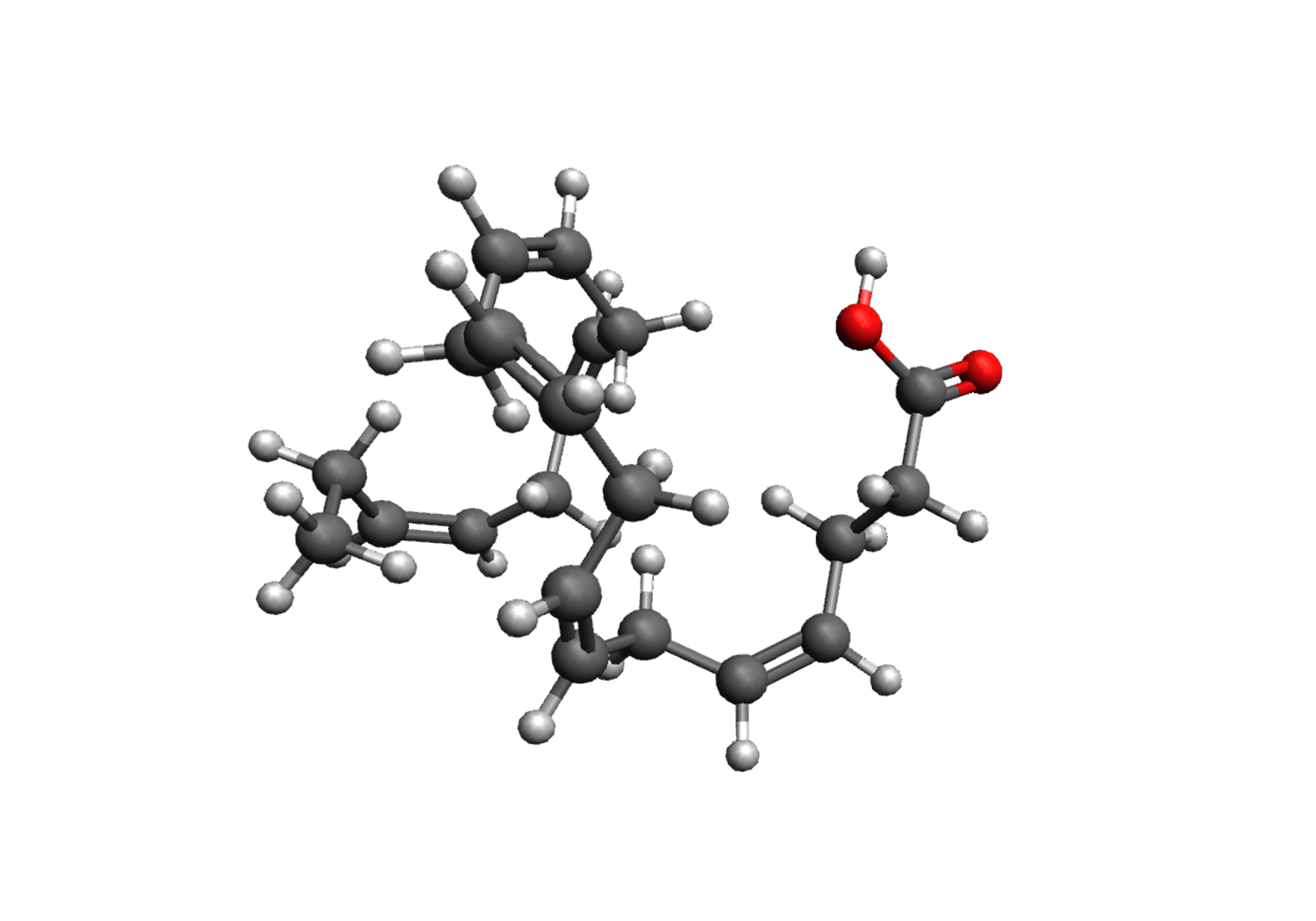
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
The brain and eyes are highly enriched with fatty acids like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). These fatty acids are essential for health eyesight and help to prevent macular degeneration, to keep the eyes lubricated, and to reduce pressure in the eyes. Omega-3 Fatty Acids from fish oil supply adequate amounts of bioavailable DHA (chemical structure shown to the right) and EPA to help protect and preserve the eyes. - Essential for healthy eyes - Protects and preserves eyesight over time - Antioxidant benefits for the eyes
Bilberry Extract

Bilberry Extract
Bilberry Extract offers a highly bioavailable form of Anthocyanins, which are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that give color to many fruits and vegetables. Anthocyanin is thought to have a host of benefits for vision and eyesight, including a relaxing effect on eye muscles, stimulation of rhodopsin regeneration, and improving retinal blood circulation. Studies have indicated positive effects on eye fatigue and dry eyes. - Highly bioavailable form of Anthocyanins - Prevents eye fatigue and dry eyes - Variety of supportive effects for preserving eye function
Collapsible content
References
References




